3 Types of Six Sigma Certifications
Six Sigma Certification gives power to employees to bring true business transformation. This in turn facilitates an enterprise to provide better products & services to its customers. Any enterprise that certifies employees (or professionals) needs to have the necessary infrastructure such as: Six Sigma training curriculum, trainers, improvement projects, experts to mentor projects, certification criteria, etc. […]
Floundering teams – A source of failure for Six Sigma Projects
Floundering teams – A source of failure for six sigma projects… many can’t believe, but it’s true. Aptly ASQ has included this topic in their SSGB BoK. The meaning of Floundering is to struggle or stagger clumsily as if confused. Floundering often results from a lack of clearly established goals, unclear tasks, discomfort with other […]
What is Sigma in Six Sigma
First time, I ever heard the term Six Sigma, I was puzzled, lost and obviously amazed. Here was a term that I couldn’t make out a bit. I felt exactly the same when I first heard H2O from my primary school science teacher. By the way, what is Sigma in Six Sigma? That’s the next question […]
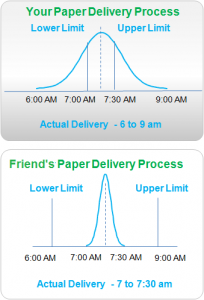
What is Six in Six Sigma?
This is the second article in the series that will help understand ‘What is Six in Six Sigma?‘ If you haven’t already read our article ‘What is Sigma in Six Sigma‘, we would like to recommend that you first do so. For now, let’s look into what is Six in Six Sigma. Let’s get started by understanding Customer […]
Why Six Sigma?
Six Sigma has evolved as a management discipline for improving processes, and providing customer delight. Some organizations like GE had adopted Six Sigma as their management philosophy. So, Why Six Sigma? Why not follow other approaches like TQM, SCM, COPC, ISO, etc. Let’s understand why many organizations choose Six Sigma over other approaches; and how they benefited. […]
Will Six Sigma help me become a better leader?
Have you ever thought about this before – Will Six Sigma help me become a better leader? Isn’t leadership a soft skill unlike Six Sigma? Six Sigma is more about playing with numbers, statistics, Minitab!!! Ask leaders of organizations that follow Six Sigma as a management philosophy, and they will disagree. Buy Canopus LSS GB Certification […]
Six Sigma & Project Management
Six Sigma & Project Management are two high trending topics of interest among professionals and organizations today. While Six Sigma is a management approach, project management principles instill the rigor of execution. Whatever is the nature of your business, innovation is critical today. In order to survive competition and be the customers’ choice, you need to […]
Six Sigma Process
Six Sigma has been a successful management approach, and a philosophy for many leading global enterprises. Let’s understand Six Sigma Process – in other words – Six Sigma Deployment Approach. While the deployment of Six Sigma depends on several factors; the following approach explains Six Sigma process in its simplest form. Six Sigma as a […]
What is Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is an approach that is part of the Six Sigma methodology, and it aims to develop products and services which operate at Six Sigma or above. What does this mean; and how is this approach different from implementing six sigma in existing products, services & processes? If you have read our […]
Lean Six Sigma Project – A Beginner’s Guide
Lean Six Sigma Project – A beginner’s guide is a series that explains how to run Lean Six Sigma projects in detail. The biggest benefit of combining Lean and Six Sigma is to deliver more value to customers and business. In order for a Six Sigma Green Belt to be successful with a project, they must […]
Define Phase of Lean Six Sigma Project – A Beginner’s Guide
Define Phase is the first phase of Lean Six Sigma Project. Following are the deliverable of this phase: Develop the Project Charter Identify the Project CTQ Create Process Maps Buy Canopus LSS GB Certification Online Course Click Here Develop the Project Charter Project Charter is an important document that summarizes the purpose, current scenario […]
Measure Phase of Lean Six Sigma Project – A Beginner’s Guide,
Measure Phase of Lean Six Sigma Project is the second phase. Following are the deliverable of this phase: Identify all possible causes (Cause & Effect Diagram) Validate Measurement System, Data Collection & Sampling Establish Process Capability Buy The Master Book for Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification CSSGB Click Here Identify all possible Causes (Cause […]