Sales Analytics Framework
The Analytics Framework for Sales aims to support a long term strategy of applying analytics in sales and to integrate seamlessly with remaining part of the organization’s analytics strategy.
There are 3 important pillars for effective deployment of Sales Analytics Framework. A framework like this, when implemented consistently, will shift Sales Analytics from a tactical business enabler to strategic business enabler.
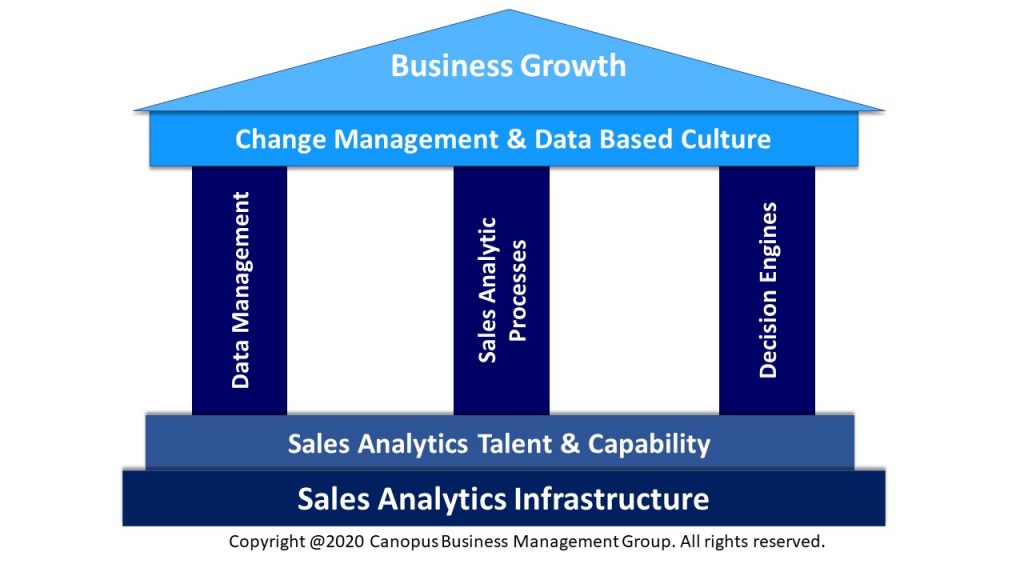
There are two important prerequisites that act as a foundation for the 3 pillars and at least one over-arching philosophy to derive best out of the Sales Analytics Framework. Let us look at what are they:
Business Benefit of deploying Sales Analytics Framework:
Business Growth
The ultimate business objective of using Sales Analytics to help meet organizational long term and short term goals such as Market Share, Revenue Growth, Profitability, Customer Retention, Cross-sell, Upsell, Referral business, etc
Overarching Philosophy:
Change Management & Data Based Culture
Ultimately leaders play a big role in deciding how the outcomes of analytics are put in practice during the decision making process. Businesses have their priorities that are time sensitive and hence sales directors play a big role in deciding how these would be actually applied. Driving a culture of data or fact based decision making within the organization should be one priority when it comes to sales analytics. The benefits of sales analytics grow multi-fold when cultural change occurs.
The Pillars:
Data Management
The first and foremost success factor in Sales Analytics is the ability to acquire, clean, organize, integrate, describe, share, govern and store data to be used for analytics. Data is usually acquired from various sources. Most organizations hit a road-block right at this stage of the journey. The next step is to clean and integrate data from various sources so as to enrich its value before performing required analytics.
Sales Analytic Processes
The core sales analytic processes include the ability to enrich the data through advanced analytics & data science and to provide, visualization, exploratory data analytics (EDA), business insights to drive sales, develop predictive models such as propensity, lead scoring, up-sell, cross-sell prediction, etc. The ongoing optimization and deployment of models in the production environment and their regular refinement are all integral to Sales Analytic Processes. The element of focus for us in Sales Analytics Processes is to answer some of the design questions keeping in mind the above end states, such as Measure of Success of Analytics Program, what analytics are we going to perform, what data and models are we going to use and how will we share the results. Learn more about How can Sales Managers leverage Analytics?
Decision Engines
How do analytics capabilities deliver business value. Traditional outcomes of analytics decision engines were linked to information delivery and visualization enabled through Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)and data mining. On the other spectrum, insight discovery and integration to decision making processes are capabilities that add business value.
The Prerequisites
Sales Analytics Infrastructure
To start with organizations can work with minimal infrastructure for analytics, but to scale analytics capability, definitely investment in infrastructure is a must. Analytics Infrastructure, not restricted to Sales Analytics, includes databases and data warehouses, statistical and data mining systems, scoring engines, grids and cloud storage ,etc., The question that new entrants frequently ask is, is it not possible to start Sales Analytics without these. The answer is that it is possible. With SaaS, it is possible to put together low cost infrastructure to get started with sales analytics. In addition to storage and handling, software tools required for sales analytics are also part of the assets. While there are standard and custom tools, the best to start would be Tableau, R, Python, SAS, RapidMiner, Orange, etc. Learn more about Guide to Selecting Sales Analytics Software Tools
Sales Analytics Talent & Capability
Quite often this is the most ignored area in analytics and is also a pitfall. Organizations get neck deep in creating analytics infrastructure, acquiring talent to manage these, and analytics talent with IT capability to deploy these tools, but they fail to understand that business users are really the ones who need upskilling. If they fail to recognize and resist the usage of analytics in their daily work management, Sales Analytics will only remain a pilot project to showcase. Lead More about What specific analytical skills are needed for Sales Managers in the era of Analytics?
Guide to Selecting Sales Analytics Software Tools

Organizations that aim to make the most out of Analytics to drive business and top line focus on Marketing Analytics and Sales Analytics. While the penetration and the adoption of Analytics in Marketing is almost as old as the adoption of analytics in business, Sales Analytics is an area that holds tremendous potential.
Sales Analytics Framework has several components and software is one of its key components. Here’s a ‘Guide to Select Sales Analytics Software Tools’:
Differentiation between Sales Analytics and Sales Reporting/Sales Intelligence
While selecting Sales Analytics Software Tools, there needs to be clarity and not ambiguity about what we wish to accomplish from the tool. Many misunderstand Sales Reporting and Sales Intelligence tools to be capable of performing advanced analytics such as Predictive or Prescriptive Analytics. While existing tools are constantly adding new functionality, it isn’t in the remit of reporting tools to perform advanced analytics.
It is good to start with reporting and intelligence tools and ripe the full benefits of better reporting before exploring advanced analytics capabilities for sales.
For example:
- SQL Server Reporting Service can be used to build dashboards for sales data for sales process management
- Sisense is a reporting tool with vast visualization capability for data that can used to manage the process
- Tableau Desktop Tool and Microstrategy Tool are capable of performing a variety of visual analysis such as trend analysis, study relationship between various factors or segments, etc that enable decision making. The purpose is to enable the users to discover insights, answer questions to drive performance.
- Alteryx Analytics Tool and TIBCO Spotfire are capable of performing advanced descriptive and predictive analytics such as scatter plot, association analysis, logistic regression, decision tree, PCA without programming. Both Alteryx & TIBCO are recognized as leaders in Gartner’s magic quadrant 2020 for data science and machine learning platforms.
Please note that there are many tools for BI in the marketplace, and I have just highlighted few to give an idea of capabilities that one may consider while selecting tools. This is not a comprehensive description of capabilities and exhaustive list of suppliers.
Customizing General Analytics Tools Vs going for Pre-built Sales Tools
There are many General Analytics Tools which have wide capability and interesting features such as the ones that you saw above. Because of the vastness of the functionality and flexibility that these tools bring-in such as accessing multiple data sources and customizing the output, they can consume additional effort to configure, selection of right metrics, and visualization required. In simple ways, implementation time can be high. On the other hand, there are tools which are built for Sales, and so they come with standard libraries of metrics, visualization charts and analytics charts that are relevant to sales.
For example:
- SAS Office Analytics and QlikSense are strong self-visualization tools for data discovery that have powerful features but are general purpose BI tools. They can be used in any where, not only Sales. For organizations that are already invested in such tools, adding Sales BI would make economic sense.
- On the other hand, MoData is a Sales Analytics specific tool for the B2B segment which is capable of creating dashboards, scorecards/performance reports, visual analysis, predictive analysis and performing sales forecasting. They have 100’s of sales specific visualization charts, thus reducing the implementation time.
Analytics Integration with Sales Systems Vs in-built Analytics functionality of Sales Systems
While we have touched on various reporting, BI and Analytics tools that can be integrated with the existing sales IT tools easily, as all tools come with the capability to integrate with multiple data sources, another option is to consider in-built analytics functionality of Sales Systems.
Many organizations that venture into sales analytics already would have sales systems (sales enablement tools) such as CRM, marketing automation, lead management, client onboarding, etc. And many of these tools are jacking up their analytics capabilities as well.
For example:
- Salesforce, a powerful CRM engine is adding AI capabilities for sales as in Salesforce Einstein.
- On the other hand, Xant is an end to end sales engagement tool that covers Sales Automation, Reporting, Intelligence, Customer Scoring, etc that can be seamlessly integrated to existing sales systems such as Salesforce, Microsoft, SAP,etc.
Learn More about Features to look for in Sales Analytics Tool
Sign-up for collaborat newsletter
